The Crypto market has evolved into a hotspot for get-rich-quick schemes. With n number of coins plying the market, it often becomes difficult to take the end call regarding their validity. Scammers are always on the lookout to steal your hard-earned money using cryptocurrency. The level of crypto scams in 2021 increased 81% compared to 2020. Keeping such things in mind, we have collated some essential information that can help you stay safe while investing in crypto.
Different Types of Crypto Scams
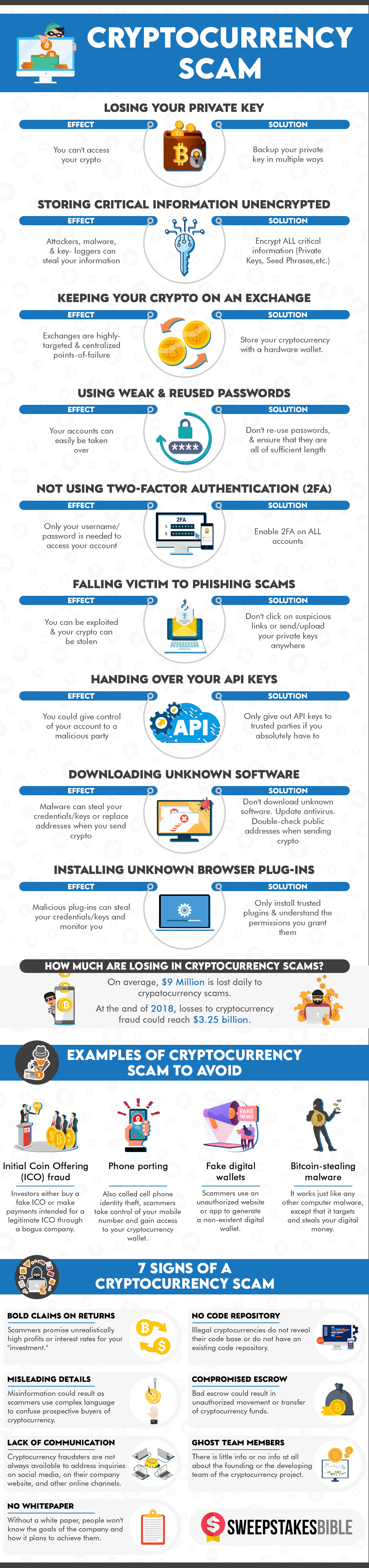
Initial Coin Offering fraud
Initial Coin Offering (ICO) is a variant of the stock exchange which works with cryptocurrencies. A new crypto token or coin is launched under ICO for making it available to the investors. However, this process is often subject to fraud, and several estimates have claimed that 80% of all ICOs are some kind of scam. ICOs are not regulated which makes them vulnerable to fraud. Scammers offering an ICO try to increase the price of crypto up to a certain level at which the entire interest is sold off. Ultimately, backers holding ICO coins see a dramatic increase in value and subsequent loss in investment.
Let’s now take a look at some of the signs indicating that an ICO is a scam:
- White papers are issued explaining the potential value of a project and why people should invest in the same. If the white paper is absent or seems unconvincing, then it is best to avoid the same.
- The project attains greater credibility when the white paper offers details on the team working with the venture. Valid ICOs offer a means for the investors to communicate with a team member. Scammers, on the other hand, try to avoid the same, be it naming members or offering a communication channel to mitigate the risk of being held accountable.
- Legitimate ICOs offer a chronological outline of funding goals and development to the potential investors. If this is lacking, then it indicates that the people behind the ICO intend to make a quick profit before eloping with the funds.
- If the ICO team reserves a certain number of pre-minted tokens to themselves, then this can serve as a warning sign. The team’s real intent is indicated by the project’s distribution schedule of tokens.
- A legitimate company will state its capital raising goal clearly on its website and white paper. If you cannot find a specific funding goal for the ICO, then chances are high that it is used to scam investors.
- ICOs with multiple tiers encourage people to lure in more investors for a greater reward and this is most likely a Ponzi or pyramid scheme. Such structure is a red flag for investors and tends to collapse when new investors drop off and the current ones cease getting payment.
Fake digital & hardware wallets
Hackers trick individuals having a hardware wallet into opting for a modified replacement to steal their crypto keys and other credentials. A package is first sent to the target consisting of the modified hardware wallet and includes a note warning about the vulnerability of the device presently in use. The users are advised to replace it with the delivered wallet following the accompanying instructions like asking the users to insert the device to their computer and input the crypto wallet recovery key. The keys are recorded and sent to the hackers on being typed in offering them a free pass to unlock the wallet on the blockchain and siphon funds.
Similar frauds can also be seen in the digital wallet scenario as the fake apps are sneaking past the vetting process of various app stores. You can take the example of the “Trezor” app which was uploaded on the Apple App store on 24th February and resembled the authentic bitcoin hardware wallet. This fake app was leveraging on the popularity of Trezor to steal the private keys and passphrases of Trezor users via phishing.
Cell phone identity theft – Identity theft is a common happening in the crypto sphere where scammers can gain access to your crypto wallet after taking control of your mobile number.
Bitcoin-stealing malware – Hackers are increasingly targeting popular operating systems by planting malware into the devices of unassuming users. Some of these viruses are specially programmed to detect crypto addresses and exchange them with the wallet addresses of hackers.
Signs of a Cryptocurrency Scam
- Digital coins that cannot be exchanged into a fiat currency might be a crypto scam. You can take the example of Bitcoin and Ethereum having local exchanges and convertible to fiat currencies. Scam dealers will allow the internal exchange of assets and this is a red flag you need to take care of while participating in crypto activities.
- Scammers often trick investors by offering crypto coins that appreciate continuously. It is important to note here that the crypto industry is extremely volatile and if you come across a constantly appreciating asset then it is most probably a scam.
- We mostly enter the crypto sphere to benefit from its high-profit potential. Scammers often take advantage of this consensus to lure in investors with unrealistic promises of high-interest rates and return on investments. If the deal sounds too good to be true, then it is most probably a scam.
- Ideally, cryptocurrency projects should be open-sourced allowing crypto owners to view the project codes and track changes as and when they happen. It is most likely a scam if the crypto doesn’t offer the links to its code.
- A legit crypto asset will never be anonymous and will offer basic information about the company’s headquarters, owner name, address, etc. If you cannot get adequate background information, then it is probably a scam coin.
- Fraudsters often cover up their unworthy or illegitimate operations using complex language. They opt for hard-to-understand crypto jargon while trying to explain the working of cryptosystems and how investors can earn a profit using their platform. These misleading details are a sign of a probable scam.
- A whitepaper serves as a reference for investors in terms of how the platform operates, other technicalities, company goals, and how the digital tokens shall be used. You need to be cautious if the ICO company fails to provide the same.
- Crypto scammers do not answer questions from their followers on different forums and social media. Unlike the legitimate ICOs, they do not post on their key communication channels or own blog sites making it difficult for investors to understand the progress.
Why Do Crypto Scams Occur?
- Losing your private key – Private keys refers to a combination of letters and numbers which act as the unique identification for users and help them engage in secure transactions. Losing your private key would mean that you will lose your assets as you will be locked out from accessing your account. Private keys are generated through random mathematical sequences making the recovery process extremely difficult. Once your private key is lost, your funds become vulnerable to anyone having access to your key. Thus, you need to be especially cautious about not sharing your private key credentials with others as this can add to the chances of your falling prey to crypto scams.
- It is advisable to safely store your private keys in a hardware wallet or even a piece of paper which can help avoid loss of keys due to server crashes or theft by cybercriminals.
- Backing up a wallet file also serves as a viable virtual backup option as it backs up your private keys. However, this should never be done in the public.
- There is also an option of using a seed phrase which is a random combination of different words that is impossible for hackers to predict. However, a seed phrase cannot be changed like your email or social media passwords and should ideally be split into two or more parts to prevent it from being stolen entirely.
- Storing critical information unencrypted – Encryption is the means of transforming information into an unreadable form that cannot be accessed by unauthorized parties. Since private keys are a pivotal part of transacting in crypto, you should always keep it encrypted to assure the recipient of integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity of data. Private keys can be backed up using seed phrases which are 12, 18, or 24-word phrases offering access to the crypto assets.
The seed phrases are used to gain access to your private keys and cryptos if you somehow forget your PIN or lose your hardware wallet. By itself, the seed phrase is not encrypted but it is always advisable to use encryption software to encrypt the file before storing it whether in a paper wallet or fire-proof steel plates. Not encrypting such sensitive information can cause your credentials to fall into the abuser’s hands.
- Keeping your crypto on an exchange – It’s common to come across news of onslaughts on crypto exchanges now and then which demonstrates its lack of adequate security. There are numerous reasons behind this ranging from technical bugs to hackers exploiting smart contracts, phishing scams, etc. Users also have to deal with the constant risk of authorities seizing the assets following which the crypto coins can be held up in litigation for years.
Given such inherent risks associated with crypto exchanges, it is always safe to store your crypto in a hardware wallet that is specially designed to store crypto private keys. You can use a hardware wallet to go online for making a transaction and can then be taken offline for maximum security. Your private keys remain unexposed as they do not reach your computer. Pin encryption adds to the level of security as the device self-destructs if someone tries logging in with the wrong pin. Viruses are usually designed to wreak havoc on system software and aren’t effective on your hardware wallet making the latter a safer bet against crypto scams. As long as your hardware wallet stays safe, you can be completely assured against fund tampering.
- Using weak and reused passwords – Weak passwords can make it easier for scammers to access your account. This also holds for reused ones which are more vulnerable to break-ins. You can enhance the strength of your password by making it long and using a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. The password you choose shouldn’t be less than 8 characters and you should also refrain from using common words found in a dictionary. Personal information like first or last name, date of birth, address, or phone number shouldn’t be used.
- Not using two-factor authentication – Fraud is rampant in the crypto sphere and users can keep themselves safeguarded by opting for a two-factor authentication procedure be it for your wallet or exchange. Apart from the password, this verification procedure offers an added layer of security in the form of a fingerprint scan, facial scan, or one-time token or code generated for each login and sent to your registered mobile number or email address.
- Falling victim to phishing scams – Phishing is a common practice undertaken to steal sensitive information like private keys, passwords, and recovery phrases for exchange accounts or cryptocurrency wallets. This is mostly done by setting up a fake website that imitates the look and feels of the real one. Though emails are the most popular tool used for phishing scams, messaging services like Discord and Telegram are also rampantly used by malicious scammers to dupe you of your precious crypto. You can keep yourself buffered from such scams by blocking, ignoring, and reporting suspicious messages and emails. Invitations to pre-sales, private trading groups, etc. should be reported to community moderators at the earliest.
- Handing over your API keys – Traders can access their exchange with the APIs to manage their portfolio, execute trades, implement complex strategies and collect data on their account using 3rd party services. API keys help identify the account that is being accessed and authenticate users. A set of API keys consists of a public and private key. The program uses the private key to sign requests while requesting access to a trader’s account. You should make it a point never to share your API keys with anyone as that would make your crypto account vulnerable to external attacks.
- Downloading unknown software – Unsolicited files or programs harbor behind-the-scenes spyware or computer viruses infamous for offering others access to your system without your knowledge. Malware can steal your keys and other sensitive credentials and also replace addresses while sending crypto. To keep things safe, you should download apps, files, and plugins from trusted sources. You need to be especially cautious of free files or software offered via email or online. Protective software like your device’s antivirus should never be deactivated and should always be updated regularly.
- Installing unknown browser plug-ins – If you are thinking of downloading plugins for viewing online content, then it is advisable to verify its legitimacy first as they often contain malware. These malicious plug-ins can monitor your every move apart from stealing your sensitive credentials and keys.
The growing popularity of blockchain technology and crypto has been accompanied by an influx of numerous cryptocurrency scams. High-tech scammers are using cutting-edge techniques to dupe investors. You can take the example of the latest Squid game scam where the developers disappeared once the currency price reached record heights and crashed subsequently. If you are thinking of diversifying your portfolio by investing in crypto then our today’s discussion will help you gauge the red flags and take a safe

